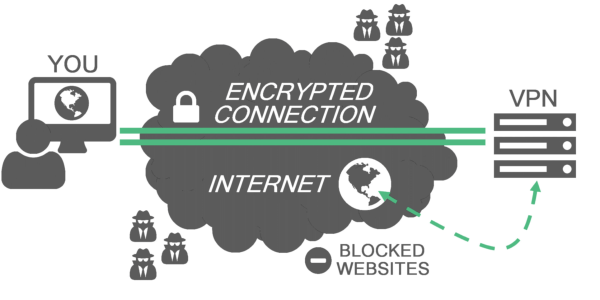
What is VPN?
A VPN, which means Virtual Private Network in full, is a technology used in networking. It creates a secure network connection over a private network owned by an ISP (Internet Service Provider) or a public network such as the Internet. Bodies such as educational institutions, large corporations, and government agencies utilize VPN technology to create a secure connection to a private network for their remote users.
Virtual Private Networks may give employees a secure access to a corporate intranet while located outside the office. They are used in securely connecting other offices of an organization that exists in other geographical locations. It creates a cohesive network. Individual Internet users may also use VPN services for securing their wireless transactions, escape censorship and geo-restrictions. VPN also used for proxy servers connection for the purpose of protecting location and personal identity. However, some websites obstruct access to known VPN technologies to disallow them from circumventing geo-restrictions.
Why Use VPN Service?
Internet service providers can sell the browsing history of their customers to the highest bidders. That has triggered most people from the United States to start checking out for the best tools in the market that can effectively mask their internet traffic and hide their browsing history.
VPNs redirect the internet traffic to disguise where a phone, computer, or any other device is after it has made contact with a website. VPNs also encrypt the information a user sends across the internet to make unreadable to individuals who intercept your internet traffic. That also includes the internet service provider. So after using a APN your ISP can not track your information.
However, you have to remember that the VPN will have your browsing history and internet traffic – not the internet service provider (ISP). Some people will interpret that as another problem. The VPN might also start selling your information to the highest bidders.
Do not panic, yet. Of course, there are many reputable VPN service providers out there. As an internet user, you should properly do your homework. Apart from ensuring that the VPN will keep your internet history and traffic private, you should ensure that there is nothing shady hidden in their terms and conditions section.
VPN Privacy Protection Mechanism
Online connections cannot be made completely anonymous by VPNs, but they can usually increase security and privacy. In order to avoid disclosure of private information, VPNs normally allow only authenticated remote access using encryption techniques and tunneling protocols.
The VPN security model provides:
- Sender authentication to disallow any unauthorized user from gaining access to the VPN.
- Confidentiality in such a way that an attacker would only see encrypted data even if the network traffic is sniffed at the packet level.
- Message integrity to discover any case of tampering with transmitted messages.
Internet Protocol Security, known as IPSec, was developed by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) for the Internet Protocol version 6. This standards-based security protocol is also widely utilized with the version 4 of the Internet protocol, known as IPv4 and the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol. The design of IPSec meets most security goals such as integrity, authentication, and confidentiality. Internet Protocol Security uses encryption in the process of encapsulating the packet of an IP inside an IPSec packet. At the end of the tunnel, de-encapsulation occurs thereby allowing the original IP packet to be decrypted and forwarded to its intended destination.
VPN Protocols
There are several VPN protocols used in securing the transportation of data traffic over a public network. These include:
IP security (IPSec)
This is used in securing communications over the Internet. IPSec traffic can use either tunneling or transport mode in encrypting data traffic in a virtual private network. What differentiates the two modes is that tunneling encrypts the entire data packet while transport mode encrypts only the message within the data packet. IPSec is often used as a security layer for other protocols.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
These protocols utilize cryptography in securing communications over the Internet. Both protocols use an authentication method known as “handshake” which involves a negotiation of network parameters between the server and client machines. An authentication process involving certificates is used in successfully initiating a connection. A certificate is a cryptographic key that is stored on both the client and server.
Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
This is another protocol used in connecting a private server with a remote client over the Internet. Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol is one of the most widely utilized VPN protocols due to its maintenance and straightforward configuration and also because of its inclusion in the Windows OS.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
This is a protocol used in tunneling data traffic between two sites over the Internet. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is occasionally utilized in tandem with IPSec in securing the transfer of Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol data packets over the Internet. However, implementing VPN using L2TP/IPSec requires the use of certificates or shared key.
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)
This is used in OpenConnect VPN and Cisco AnyConnect VPN to solve the issues SSL/TLS has with tunneling over Unified Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Secure Shell (SSH) VPN
It offers VPN tunneling to secure remote connections to inter-network links or a network. The server of OpenSSH provides a limited number of simultaneous tunnels. The virtual private network feature itself doesn’t support personal authentication.
VPN technology employs advanced encryption to prevent any unintentional interception of data between private websites and ensure security. All traffic over a virtual private network is encrypted using algorithms to secure privacy and data integrity. The architecture of VPN is governed by a strict set of standards and rules to ensure a private communication channel between websites. In deciding the scope of a VPN, ongoing monitoring of network traffic across the network firewall, and implementing and deploying a VPN, network administrators are saddled with such tasks to oversee these activities. Running a virtual private network requires the services of network administrators to be continually aware of the scope and the overall architecture of the VPN to ensure communications are kept private.
Is VPN really effective in protection of internet privacy
Actually, a VPN can effectively shield you from the bad cable companies. However, they are also in a better position to do the things that influenced you to search for their services. They are likely to track your movements and activities online. Therefore, you should only select a trustworthy VPN service provider.
Check whether the VPN will keep a log of your activities. Most privacy-focused virtual private networks are intentionally upfront about no-log policies. That is because they want to be clearer to the law enforcement agencies around the world that they cannot produce records of their customer data including when served with subpoena or warrants. It is therefore important you check the terms of service. They will help you understand the VPN’s policy about when they can disclose your logging information.
You have to understand that even VPNs are not foolproof. Companies can misrepresent their logging practices or accidentally store their data for longer periods than necessary. What’s more, studies show that scams are more common among VPNs and some services never offer the features they claim to offer.